Prompt Graph Design
Method II ·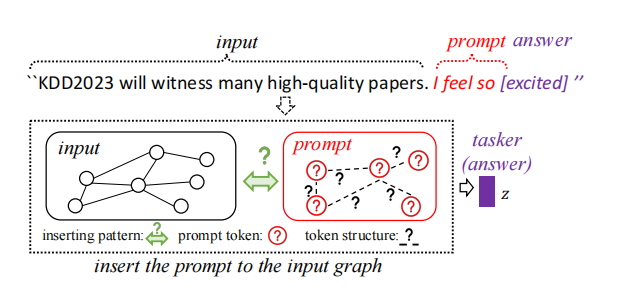
We first unify the format of graph prompts and language prompts with the prompt token, token structure, and inserting pattern. In this way, the prompting idea from NLP can be seamlessly introduced to the graph area.
To seamlessly transfer the prompting idea from NLP to the graph domain, we propose to unify NLP Prompt and Graph Prompt in one perspective. Having compared the demand of NLP and graph area as shown in Figure 2, we found that the prompt in NLP and graph areas should contain at least three components:
- prompt token, which contains the vectorized prompting information with the same size as the input word/node vector;
- token structure, which indicates the connection of different tokens. In the NLP area, prompt tokens (a.k.a prompt words) are preset as a linear relation like a sub-sentence or a phrase; whereas in the graph domain, the connections of different tokens are non-linear and far more complicated than NLP prompts;
- inserting pattern, which presents how to add the prompt to the input data. In the NLP area, the prompt is usually added in the front or the back end of the input sentences by default. However, in the graph area, there are no explicit positions like a sentence to joint graph prompt, making the graph prompting more difficult.
